The use of humanized mice, which engrafted with human tissues, cells, and/or genes, has been a valuable tool for studying preclinical aspects of human ailments, as the research results these models provide have helped us understand the development of a specific infection and how various pathological events are exhibited at the cellular level.
Over the last 20 years, the exceeding implementation of humanized models in biomedical research has facilitated discernment of human physiology, infection pathology, and host immunology at molecular, cellular, and organ system levels. The primary purpose of biomedical research is to vanquish human infectious agents and diseases that has been improved with the implementation of humanized mouse models.
Compared to other primates (including conventional mice), the humanized mouse features greater reproductive capability, translational potential, and repeatability of data. These humanized mice are more economical and safer under the ethical concerns. In addition, the development of translational medicine has gained significant improvement with the implementation of humanized mice.
Application of Different Humanized Mice in Different Research Aspects
1. Hu-PBMC for GvHD research, such as HIV/AID, etc
For in vivo research of human immunological circumstances during a specific disease or novel vaccine development, a mouse model, based on immune-deficient xenogeneic-GvHD, is injected with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and is proved to be a substantial tool. The human cell engraftment improvised with the implementation of humanized mouse with deleted interleukin-2 (IL-2RY: NOD-SCID IL-2RY or BALB/c-Rag2 IL-2RY) (Ali et al., 2012). For the study of pathological circumstances and therapeutic trials in HIV infection, the NRG-hu HSC mice model (reconstituted with human HSC) is suitable.
2. Hu-HSC (Hu-CD34) for tumor research, adoptive cell transfer, etc.
In oncological research, humanized mice with CD34+ cells are suitable for their stable engraft of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC), and they are named as a huCD34+-HSC mouse. They consistently produce human cell lineage for up to 9 months.
3. Hu-NOG for the study of liver, human hematopoietic, and immune system research.
Immunodeficient mice present hematopoietic cells multilineage of humans, which process cell reconstitution capability, and can be engrafted with liver, skin, pancreas, blood cancer, and tumorous mass. Humanized NOG mouse is one kind of immunodeficient mice and is best for hematopoietic, immunological, and tissue grafting studies.
How Are Humanized Mice Made?
1. Hu-PBMC
The peripheral blood mononuclear cells of humans are injected in immune-deficient mouse intraperitoneal or intravenously. The injection of human tumorous mass engrafted or HIV-infected cells are then use for evaluation.

2. Hu-HSC
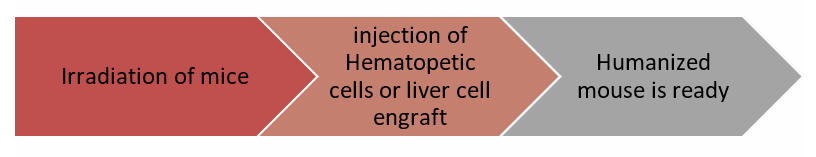
Immune-deficient mice have undergone irradiation followed by engraftment of human cells (CD34+) intravenously. After 12 to 14 hours, humanized mice which have CD45+ cells (T and B-lymphocytes) are ready for implantation of tumor cells PDX or CDX.

3. Hu-NOG
An immunodeficient mouse model is produced via radiation and engrafted with hematopoietic cell lineage of human, liver tissue, or any other tissue of concern.
Significance of Humanized Mice
Cyagen humanized mice play a significant role for biological research, including regenerative immunogenic, and translational medicine. In the past few years, there have been important accomplishments in the implementation of humanized mice in developing vaccine for human ailments, for examples, Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), Flavivirus, HIV-1, CE-antigen, and coronavirus (SARS-CoV).
A great number of novel vaccine improvement experiments are developing in humanized mice, which involve the reconstitution of immune cells. Cyagen’s humanized mice are suitable for immunodynamic and immunomodulatory researches, the study of pathological and oncological circumstance, pharmacodynamic trials, and prediction of clinical responsiveness of a pathogen.