Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are those antibodies that have two binding sites directed at two different antigens or two different epitopes which are on the same antigens. The clinical therapeutic effects that BsAbs have are way superior to that of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). They have broad applications for tumor immunotherapy and the treatment of other diseases. As antibodies keep experiencing progress with protein engineering and recombinant DNA technology, various platforms for generating different types of BsAbs based on novel strategies and uses have been established. Different commercial technology platforms have been used to create and develop BsAbsbased on the heterologous recombination of heavy chains and matching of light chains. Three kinds of BsAbs have received market approval and other bispecific antibody types that are over 110 are undergoing different stages of clinical trials.
Rabbit monoclonal antibody has been used in carrying out research for the diagnosis and treatment of different kinds of diseases with some types of cancer which acts on the antigens. However, the natural bispecific antibody was first described in the allergic patients who received two therapeutic injections having two different allergens. For the bispecific antibody production on rabbit monoclonal, there have not been any scientific reports of bispecific antibodies in animals. A natural bispecific antibody can as well be generated in the New Zealand white rabbits through immunizing with synthesized conjugates. The components that were concurrently used for the immunization of the animals, the antibodies showed bispecificity.
Applications of bispecific antibodies
The application of bispecific antibodies is usually based on the BsAbs production platform with different applications such as oncology, immunology, hematology, ophthalmology, osteology, pulmonary and respiratory diseases, pretargeting systems, diagnostics, and gene therapy.
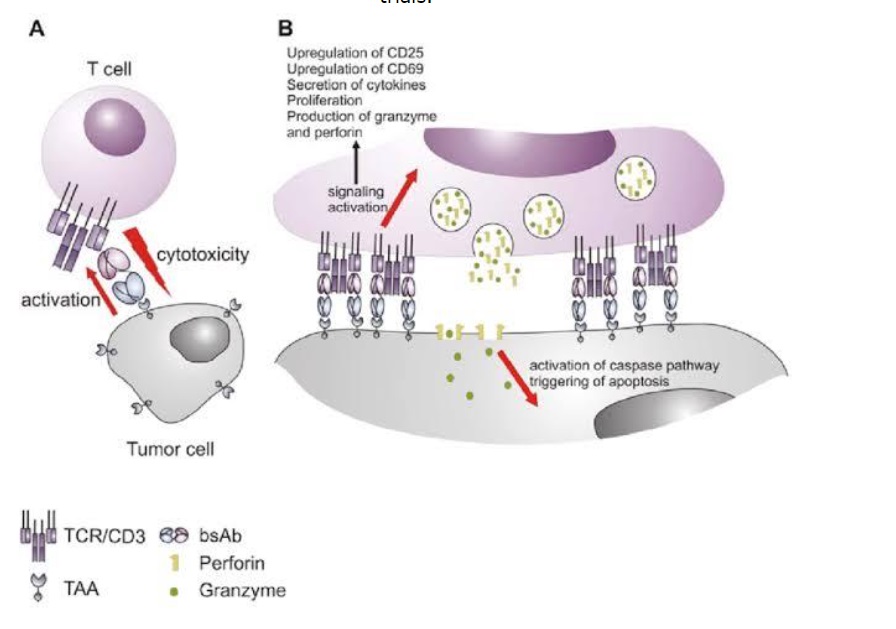
- Application of bispecific antibodies in oncology: the application of bispecific antibodies is well known in the treatment of cancer. BsAbs are engineered to interfere with the signaling pathways that are involved in the development of a tumor or made to redirect cytotoxic immune cells such as the T cells and NK cells that kill tumors. Radioactive therapeutics can also be delivered to the tumor cells to kill them. BsAbs can also signal pathway interference, the delivery of payloads, and the recruitment of immune cells to apply to oncology.
- Application in immunology: the immune system is known for maintaining human health. Sometimes, immune malfunctioning or excessive responses from the immune system can result in tissue damage and destruction, and affect organ growth and its functions. When there are immunological disorders such as chronic inflammation, autoimmune diseases, immune deficiency, or transplant rejection, BsAbs have the receptor capability of signaling the interference and can be applied to immunology.
- Application in Hematology: hematology deals with blood diseases that affect blood component production or other problems in the blood coagulation. Some of the blood diseases that are related to hematology are blood cancer, bleeding disorders, and blood clots. The bispecific antibody has been applied to hematology and for other blood treatments as well.
- Application of bispecific in pulmonary and respiratory diseases: the main pathogenesis of pulmonary and respiratory diseases is infection and inflammation. These diseases are caused by unwanted immune responses, excessive inflammation, or an aberrant wound healing process. With the application of bispecific antibodies for this infection and inflammation, it can bind ligands or receptors and block unwanted signaling pathways.
- Application of bispecific antibody in pretargeting system: as bispecific antibody has the capacity of binding two different targets together, they can be widely used in the payload delivery such as drugs, radiolabels, or small molecules.
- Application of bispecific antibody in osteology: functional crosstalk between osteoclasts and osteoblasts is very essential for remodeling of bone. In this case, a bispecific antibody that forces the association of protein is a good strategy for carrying out osteology research. An instance of this is the suggestion that the receptor activator of NFKB Ligand is a crucial factor of osteoclastogenesis in the living organism. These malignant diseases can be treated with the generated targeting RANKL and RANKL/RNAK signaling pathways.
- Application of bispecific antibody in diagnostics: in several applications, the bispecific antibody has been used in diagnostics such as immunoassays, radioimmunodiagnosis, and immunohistochemistry. With the application of bispecific antibodies as a recombinant antibody protocol, detection is more sensitive, rapid, and specific. The application of bispecific in diagnostics also helps to avoid BsAb diagnostic reagents in batch-to-batch variations. Bispecific meditated reactions have improved the signal-to-noise ratio as well as simplified procedures in the case of immunohistochemistry and immunodiagnostic assays.
- Application of bispecific antibodies in Gene therapy: gene therapy is the therapeutic approach that involves the transfer of genes into patients’ cells for therapeutic purposes. To cure inherited diseases using gene therapy, human genes can be transferred for gene correction. Introducing therapeutic genes from various species can serve as a benefit in the treatment of many different diseases. The bispecific antibody can be applied as the therapeutic gene that is transferred or developed as adapter molecules in gene therapy.
Conclusion
The characteristics of the bispecific antibody of binding two different antigens have made it have a wide range of clinical applications as a targeting agent for immunodiagnosis and therapy. Rabbit monoclonal antibody that binds to single antigens has also played a significant role in the laboratory research of bispecific antibodies for diagnosing and treatment of certain diseases. As rabbit antibody is developed in the laboratory, it is also believed that bispecific antibody is constructed artificially by recombinant DNA or cell fusion technologies. However, there is a class of natural bispecific antibodies that were obtained from allergic patients who were receiving therapeutic injections with two different allergens during specific immunotherapy.