Vitamin B12 is vital for creating and maintaining nerve and red blood cells, it supports the nervous system, and it helps create DNA, the basis of all cells. With age, it can become harder to absorb this vitamin. It can also happen if you have had weight loss surgery or another operation that removed part of your stomach, or if you drink heavily.
Without treatment, vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to anemia. It can also result in nerve and brain damage. To check the level of Vitamin B 12, you must undergo Vitamin B 12 test. And, before undergoing the test, you must enquire about the Vitamin B12 test cost.
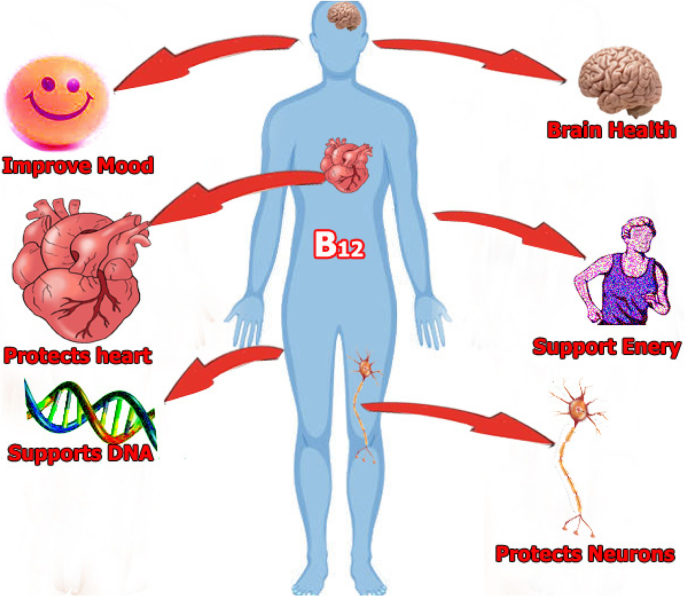
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that’s essential for several aspects of health.This vitamin is involved in forming DNA and red blood cells, as well as necessary for brain function, heart health, energy production, and more. It’s found naturally in many animal products and sometimes added to fortified foods.
If you need to go for the Vitamin B12 test, reach out to the best diagnostic centre near me.
Understanding Vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 is mainly found in animal products, especially meat and dairy products. However, for those eating vegan diets, fortified foods can be good sources of this vitamin.
You may develop a vitamin B12 deficiency if your body doesn’t produce enough intrinsic factor or if you don’t eat enough vitamin B12 rich foods.
The amount of vitamin B12 an individual needs per day will depend on their age. People also need more B12 during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency
A person with vitamin B12 deficiency may develop anemia and other symptoms. Low levels of B12 can lead to fatigue and weakness, constipation, loss of appetite and weight loss, problems with balance, depression, problems with thinking, and a sore mouth or tongue
In infants, signs of a deficiency include not growing or developing at the expected rate, problems with movement, and megaloblastic anemia.
If a person does not have enough vitamin B12, their body cannot make enough red blood cells. This can result in anemia. The hallmark symptom of B12 deficiency is megaloblastic anemia, in which the red blood cells are immature and larger than usual. This affects their ability to deliver oxygen effectively to the body.
A Vitamin B12 deficiency can also lead to neurological symptoms, such as numbness and tingling in the hands and feet, problems with thinking and memory, confusion, problems with balance and changes in gait and other movements
Causes of Vitamin B12 deficiency
A B12 deficiency can occur if a person does not consume enough of the vitamin in their diet or if their body cannot absorb it effectively during digestion.
When a person consumes food that contains vitamin B12, the body takes two steps to absorb it. First, hydrochloric acid in the stomach separates it from the protein it binds to in food. Then, vitamin B12 combines with another protein that the stomach produces, called intrinsic factor. Then, the intestines can absorb it.
Here mentioned are some of the possible causes of Vitamin B12 deficiency:-
Pernicious anemia – It is an autoimmune disease that affects the gut’s ability to digest vitamin B12. When a person has pernicious anemia, their immune system creates antibodies that attack the stomach’s lining. There, they damage cells that produce intrinsic factor. If the stomach cannot produce intrinsic factor, the intestines will be unable to absorb vitamin B12.
Bowel problems – Some people may have problems absorbing vitamin B12 into their bloodstream because of a condition that affects their stomach or small intestine. Possible causes include crohn’s disease, celiac disease and surgery that reduce the size of the stomach or the length of the intestine. These people can experience malnutrition because they cannot absorb enough vitamins, water, and other nutrients.
Diet – People who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet may have a higher risk of B12 deficiency. During pregnancy, this may increase the risk of neurological damage in a fetus. While some plant foods contain vitamin B12, it is often in a form that the body cannot absorb efficiently, according to research published in 2013.
Medications – Some medications can affect the body’s ability to digest vitamin B12, leading to a deficiency. Examples include proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and Histamine H2 receptor agonists (H2 blockers), which doctors prescribe to treat indigestion, heartburn, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). PPIs prevent the stomach from producing acid, but the body needs acid to absorb vitamin B12.
Diagnosis of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
To evaluate for a vitamin B12 deficiency, a doctor will likely ask about symptoms and carry out a physical examination. Also, conduct a blood test to measure B12 levels. And, check for anemia and perform other tests to rule out other conditions .
Some people will have a B12 deficiency but no symptoms. A doctor may recommend regular testing for people with long-term gastrointestinal problems to ensure a deficiency does not develop. Getting an early diagnosis can help prevent long-term complications.
Treatment for Vitamin B 12 Deficiency
Treatment will depend largely on the cause of a deficiency. Options include increasing Vitamin B12 intake through intramuscular injections, oral medicine and adding foods that are rich in B12 to the diet. Some people may need regular injections for the rest of their life.
Tips to Prevent Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Most people can prevent vitamin B12 deficiency by eating enough meat, poultry, seafood, dairy products, and eggs.
If you don’t eat animal products, or you have a medical condition that limits how well your body absorbs nutrients, you can take vitamin B12 in a multivitamin or other supplement and foods fortified with vitamin B12. If you are very low in this vitamin, you can get higher-dose vitamin B12 shots.
If you choose to take vitamin B12 supplements, you must inform your doctor so that he can tell you how much you need, or make sure they won’t affect any medicines you are taking.